The Difference Between Digital and Analog HVAC Gauges
In any HVAC repair, installation, and maintenance shop, you’ll find a variety of equipment used to monitor and maintain heating and cooling systems. If you’re on the path to becoming an HVAC technician or you simply want to perform your repairs, you’d better learn how to use refrigeration gauges.
A powerful product designed to be easy to use for both techs and consumers alike, refrigeration gauges – also known as manifold gauges – function as diagnosis and service devices. If you scroll through the pages on an automotive or HVAC supply website, you’ll find countless products in stock claiming to make your job easier.
These tools come in two main forms – analog and digital. Each has its advantages and disadvantages, depending on what you request of them. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between these gauge systems, how to use them, and which ones will work best for your needs.
What is an HVAC Manifold Gauge?
HVAC manifold gauges are an extremely useful tool for providing accurate measurements as to how well your system is functioning. Whether you simply need to troubleshoot your heating and cooling system or there are more serious problems at hand, they make any technician’s job easier.
However, this equipment won’t be very useful to you unless you understand how the different tools work. Reading them requires a bit of technical know-how, so let’s cover that topic next.
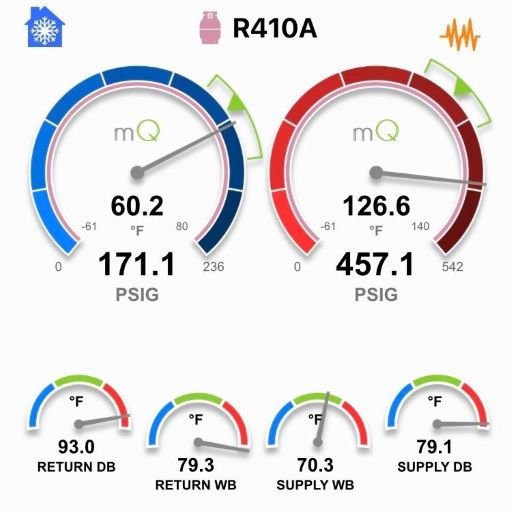
Analog vs. Digital
Analog Pros
Analog gauges, also known as mechanical gauges because of their mechanical gear and shaft assembly, are the more common older style gauges you’ll find on the market. As compound gauges, analog gauges measure pressures above and below the zero point and require manual calibration.
Analog gauges consist of two gauges, a red high-pressure gauge, and a blue low-pressure gauge, connected by a central manifold with several ports. More affordable and easier to maintain, many industry professionals prefer this tried-and-true gauge tool.
Analog Cons
However, analog refrigeration gauges require users to read between the lines to determine the precise pressure reading. Then, users have to use a pressure-temperature (P/T) chart to obtain a temperature equivalent, then take a real temp reading and subtract those two numbers. It’s very possible to misread a number or make a mistake in math. Even highly trained technicians can get inaccuracies as high as four or five degrees.
Digital Pros
Digital gauges work along the same principles as analog gauges but are far more effective for accurate pressure readings. Digital gauges have LCD screens that provide tons of information and have pressure-temperature (P/T) charts for different types of refrigerants.
These refrigeration gauges are necessary for technicians who need accurate superheat and subcooling readings. They have temperature clamps that connect to the liquid line and suction line and provide live, instant readings. Because the margin for error is so low compared to an analog HVAC gauge, they’re preferred in more commercial/industrial settings.
Digital Cons
However, digital equipment is far more expensive than HVAC tools. Depending on your location and your bank account, you may be better off with a traditional gauge. Automotive industry professionals, as opposed to HVAC techs, may be more likely to use these tools as well. But if you want to make your job easier in either role, you might be better off spending the extra money on a digital gauge.
Industry Professionals’ Opinions
Many technicians are required to use specific digital gauges to keep the rights to sell specific brands. For the most part, these policies exist to prevent warranty returns due to improper charging methods. Thus, requiring digital gauges is more of an attempt to combat warranty returns than to prevent actual problems.
Still, many technicians prefer the more affordable side of analog gauges for their tools on any given job. For instance, if a system has severe burnout, they don’t necessarily want to plug their $350 set of tools into it if they could risk a lot less with an analog system. Sure, it may go a lot faster, but is it worth the financial risk?
Reading an HVAC Manifold Gauge
Have a job to do and need to know how to read your HVAC tools?
First, attach the high-pressure side of the cooling unit to the red port on the manifold gauge. Red usually indicates high pressure on most gauges, so this tip works pretty universally. Then, connect the proper hose for tolerating pressure using the fittings that come with it to the port on the cooling line. Typically, the high-pressure port uses a different-sized hookup than the low-pressure side to prevent inaccurate hookups.
Your next step is to attach the low-pressure line to the blue side of your HVAC gauge. After you connect the low-pressure side to your blue low-pressure hose, it’ll enable the proper flow of vacuum pressure so you can evaluate the system’s current vacuum pressure.
Then, attach waste hoses or vent hoses to the center of the manifold. If the unit discharges or vents Freon, you may need a larger low-pressure hose. Then, you can recover refrigerant that would otherwise spill.
Attach any other gauges and the micron meters (for vacuum pressure) to the ports. Afterward, you should be done with the setup and able to take readings.
Remember: these tools come in a variety of brand names. Each brand has its advantages and disadvantages – especially if you are in the automotive industry as opposed to the HVAC industry.
HVAC Tools – Gages That Work for Your Needs
With their price discrepancies, you’ll probably find it difficult to choose which gauge or which gauge brand is best for your specific needs. There are several manifold gauge products on the market, some with features that may suit you as a technician, and other features more aligned with homeowners.
For most people who use them often, it’s never as easy as buying a single set. You’ll often find automotive and HVAC techs carrying multiple sets around so they can work on different types of systems.
Once you understand how to search for, access, purchase, and operate these HVAC manifold gauges, you should have no problems understanding a cooling system’s needs. However, you may need to reach out to a professional to help you solve your HVAC issue. Plus, refrigerants require proper licensing to handle.