Essential Parts of an Home AC System Pics: A Quick Guide
Looking for a clear visual breakdown of the parts of an home AC system pics? You’ve come to the right place. In this guide, we’ll walk you through each essential component with detailed pictures and explanations. Whether you’re aiming to understand how your system works or identify parts for maintenance, this article has got you covered.
Key Takeaways
Home air conditioning systems operate by transferring heat and humidity from indoor air to the outside, utilizing key components such as evaporator coils, compressors, and condenser coils.
Regular maintenance of air conditioning systems, including cleaning air filters and identifying refrigerant leaks, is crucial for optimal performance and longevity.
Investing in high-efficiency AC units and smart thermostats can lead to significant energy savings and improved indoor comfort while reducing environmental impact.
Quick Links:
Overview of Home Air Conditioning Systems
Home air conditioning systems operate by transferring heat and humidity from the indoor air to the outside, thereby providing cooled air indoors. This continuous cycle involves cooling indoor air, absorbing heat into the refrigerant, and releasing that heat outdoors. The primary aim is to maintain a comfortable living environment by controlling indoor temperature and humidity.
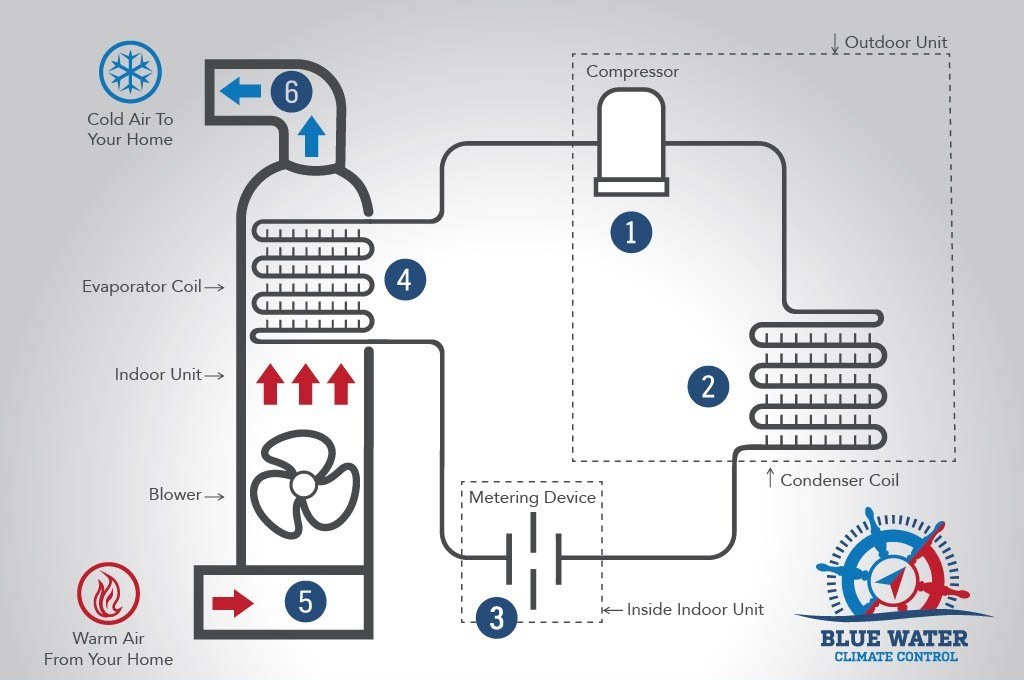
A typical central air conditioning system consists of several key elements: a thermostat, an outdoor unit with a compressor and condenser coil, an air conditioning unit with an evaporator coil, and an indoor unit with a blower. In a split-system air conditioner, the indoor unit contains the evaporator coil and blower, while the outdoor unit houses the compressor and condenser coil.
Systems can vary, including split-systems, packaged systems, and ductless systems, each meeting different needs. No matter the type, air conditioning systems greatly enhance indoor comfort and the overall living experience.
Key Components of an AC System with Pictures
An air conditioning system comprises several key components working together to cool your home. The four primary components are the evaporator coils, compressor, condenser coils, and expansion valve. Each of these parts plays a critical role in the refrigeration cycle, which is the process used to transfer heat from a cool area to a warmer area by manipulating refrigerant pressure through compression and expansion.
Knowing these components helps in diagnosing issues and performing maintenance. The main components of an air conditioning system include condensers, compressors, thermostats, and refrigerants.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these major parts.
Evaporator Coils
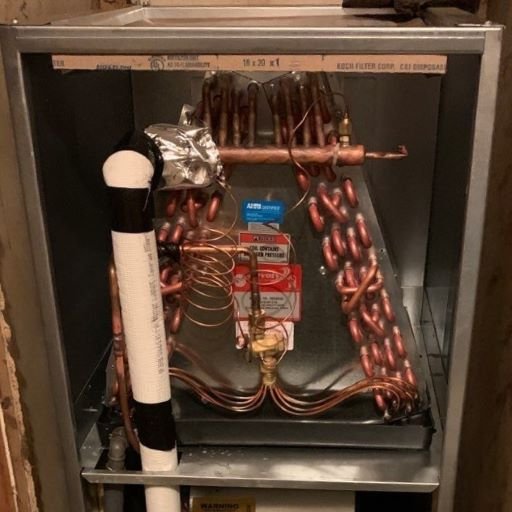
Evaporator coils play a crucial role in the indoor unit of an air conditioning system. Located within the air handler or furnace, these coils absorb heat from the indoor air, which helps cool the air before it is circulated throughout the home. When warm air is pulled into the system, the evaporator coils remove heat, thereby lowering the indoor temperature. The cooled air is then distributed back into the living spaces, providing a comfortable environment.
Typically made of copper due to its excellent thermal conductivity, evaporator coils are essential for the cooling process. A faulty evaporator coil can cause a reduction in cooling capacity. Additionally, it can result in increased energy bills. Dust and dirt buildup on the coils can also cause poor energy efficiency, making regular maintenance crucial to ensure the system operates optimally.
Compressor
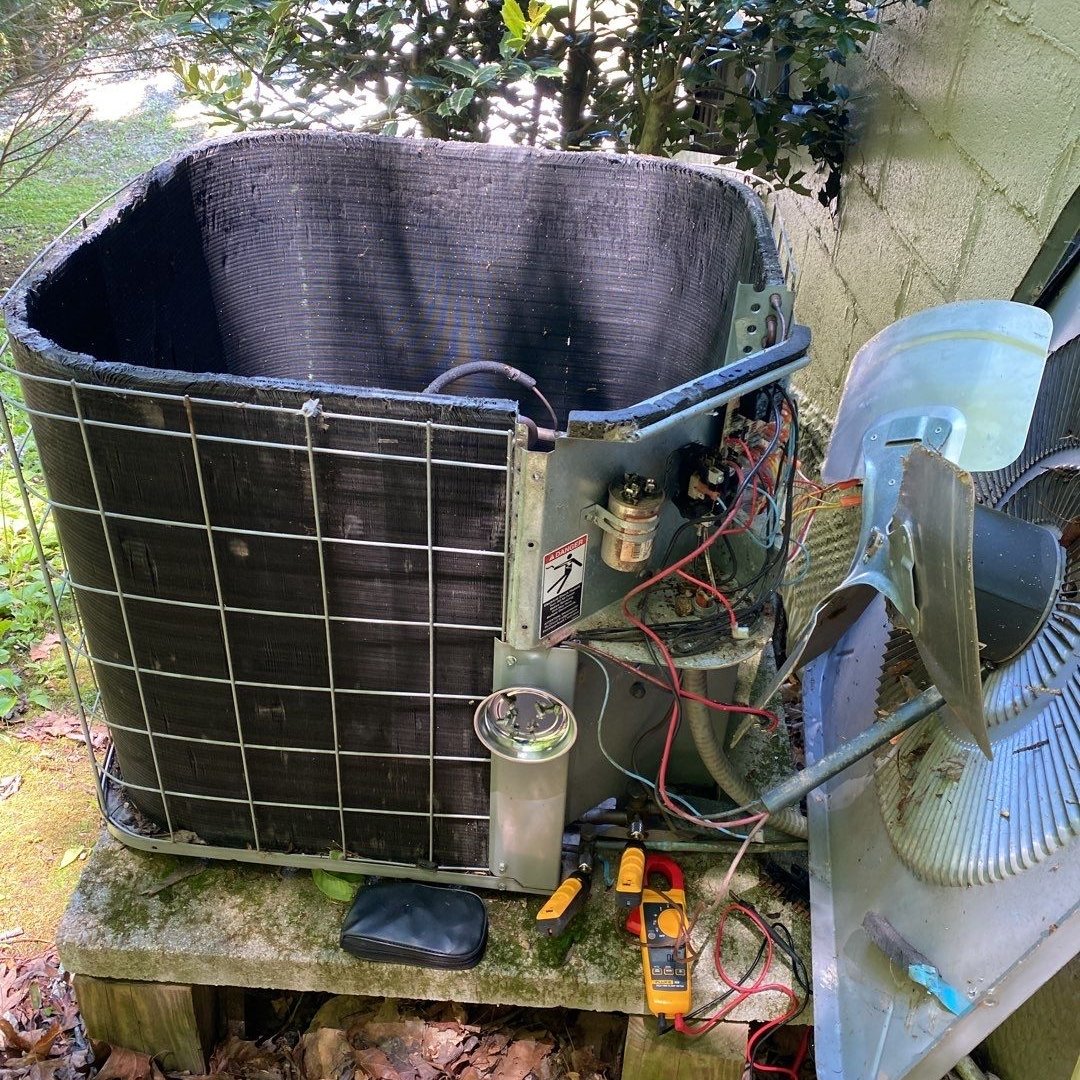
The compressor is the powerhouse of the air conditioning system, responsible for circulating and pressurizing the refrigerant. Located in the outdoor unit, the compressor’s primary function is to compress the refrigerant gas from the evaporator coils, increasing its pressure and temperature before it moves through the condenser coils.
The compressor is the costliest part to repair or replace, making its maintenance vital for the system’s longevity. A damaged compressor can result in significant repair costs and reduced efficiency, highlighting the importance of regular professional check-ups and timely maintenance.
Condenser Coils
Condenser coils are located in the outdoor unit and are responsible for removing heat from the refrigerant and releasing it outside. These coils absorb heat through metal fins, causing the refrigerant to change from a gas to a liquid state in the condensing unit. This process is crucial for the refrigeration cycle, as it allows the system to expel the absorbed heat from your indoor environment.
Minor blockages in the condenser unit can reduce performance and increase energy costs. Keeping the condenser unit free of debris prevents these issues and ensures efficient operation.
Expansion Valve
The expansion valve regulates the pressure drop, converting liquid refrigerant into vapor in the evaporator coil. It allows a limited amount of liquid refrigerant to enter the evaporator coil, enabling it to expand and significantly drop in temperature. This pressure regulation is crucial for the cooling process.
There are different types of expansion valves, such as Thermal and Capillary Tube variants, which manage the refrigerant flow from high to low pressure effectively. A malfunctioning expansion valve may lead to insufficient cooling, with the air conditioner potentially blowing hot air instead of warm air.
Replacing an expansion valve typically incurs costs between $200 and $700, with an average replacement price around $400.
Supporting Parts of an AC System with Images
While the major components of an air conditioning system handle the primary function of cooling, several supporting parts ensure the system operates smoothly. These components include the blower fan, thermostat, and air filter. Each of these components plays a role in maintaining airflow, regulating temperature, and ensuring air quality.
Blower Fan
The blower fan is crucial for circulating cool air throughout the home. Situated in the indoor unit, it moves air through the system, ensuring even distribution of cooled air. The blower fan is particularly important when set to continuous operation, as it helps maintain a consistent indoor temperature and comfort level.
Thermostat
The thermostat acts as the brain of the air conditioning system, monitoring and regulating indoor temperature. It signals the system to operate when the room temperature deviates from the desired setting, ensuring a comfortable environment. Thermostats use temperature sensors to control indoor cooling, helping to maintain the desired temperature conditions.
Smart thermostats go a step further by optimizing energy usage based on occupancy patterns, enhancing both comfort and efficiency. Installing these devices allows homeowners to program temperature settings based on daily schedules, significantly optimizing energy use.
Air Filter
Air filters maintain air quality by filtering dust and debris from the air circulating in the system. Regular maintenance and replacement of air filters are essential to prevent the accumulation of dust and other allergens, which can lead to decreased airflow and reduced system efficiency.
Indoor and Outdoor Units Explained
In split air conditioning systems, the indoor and outdoor units have distinct yet complementary roles. The indoor unit typically includes a furnace or fan coil, housing the evaporator coil and helping circulate air throughout the home. Meanwhile, the outdoor unit contains the condenser coil and compressor, which work together to expel absorbed heat outside.
The circulating fan is essential for both air conditioning and heating, drawing air through filters and distributing it throughout the home. Understanding these units’ functions can help homeowners better maintain their systems and ensure efficient operation.
Indoor Unit
The indoor unit is usually located inside the home, often centrally like in a hallway or near main living areas. It includes components such as the evaporator coil, blower fan, and sometimes a furnace or fan coil. The evaporator coil absorbs heat from the indoor air, causing the refrigerant to transition from a liquid to a gas. This heat absorption process is a critical part of the refrigerant cycle.
The evaporator coils work in conjunction with the condenser coils in the outdoor unit to facilitate heat exchange, ensuring the indoor environment remains cool and comfortable. Proper placement and maintenance of the indoor unit are essential for optimal performance.
Outdoor Unit
The outdoor unit, located outside the home, includes the condenser coil and compressor. The fan in the outdoor unit pulls air over the condenser coil to remove heat from the refrigerant, aiding in the cooling cycle. This process is crucial for maintaining the efficiency of the entire system.
Keeping the outdoor unit free of debris and ensuring it has adequate airflow can prevent performance issues and prolong the system’s lifespan. Regular maintenance and inspections are necessary to keep the outdoor unit functioning correctly and efficiently.
The Refrigerant Cycle with Diagrams
The refrigerant cycle is the backbone of any air conditioning system, enabling the transfer of heat from the indoors to the outside environment. This process involves several steps and components working together to ensure efficient cooling.
Refrigerant Lines
Refrigerant lines are essential for moving refrigerant between the indoor and outdoor units in an HVAC system. These lines, commonly made of copper, transport refrigerant between the indoor evaporator coil and the outdoor condenser coil. Regular inspections help prevent leaks. Maintenance is also important to extend the life of the refrigerant lines.
Leaks in refrigerant lines can be caused by wear, corrosion, or physical damage, leading to reduced system efficiency and potential repairs. Identifying and addressing these issues early can save homeowners from costly repairs and system downtime.
Heat Transfer Process
The heat transfer process in an air conditioning system involves the refrigerant absorbing heat from the indoor air and expelling it outside. Evaporator coils play a critical role by absorbing heat, causing the refrigerant to evaporate and transition into gas form. The compressor then pumps this gaseous refrigerant, pressurizing it and allowing it to circulate through the system.
The condenser coils release the absorbed heat from the refrigerant, transitioning it back into liquid form and expelling the heat into the outdoor environment. This continuous cycle of heat absorption and expulsion ensures that the indoor environment remains cool and comfortable.
Common Issues and Maintenance Tips
Regular maintenance of an HVAC system is crucial to ensure efficient operation and minimize energy usage. Common issues include dirty or damaged coils, weak airflow, and malfunctioning fans.
Regular vent cleaning and professional servicing can help mitigate these problems and keep the system running smoothly.
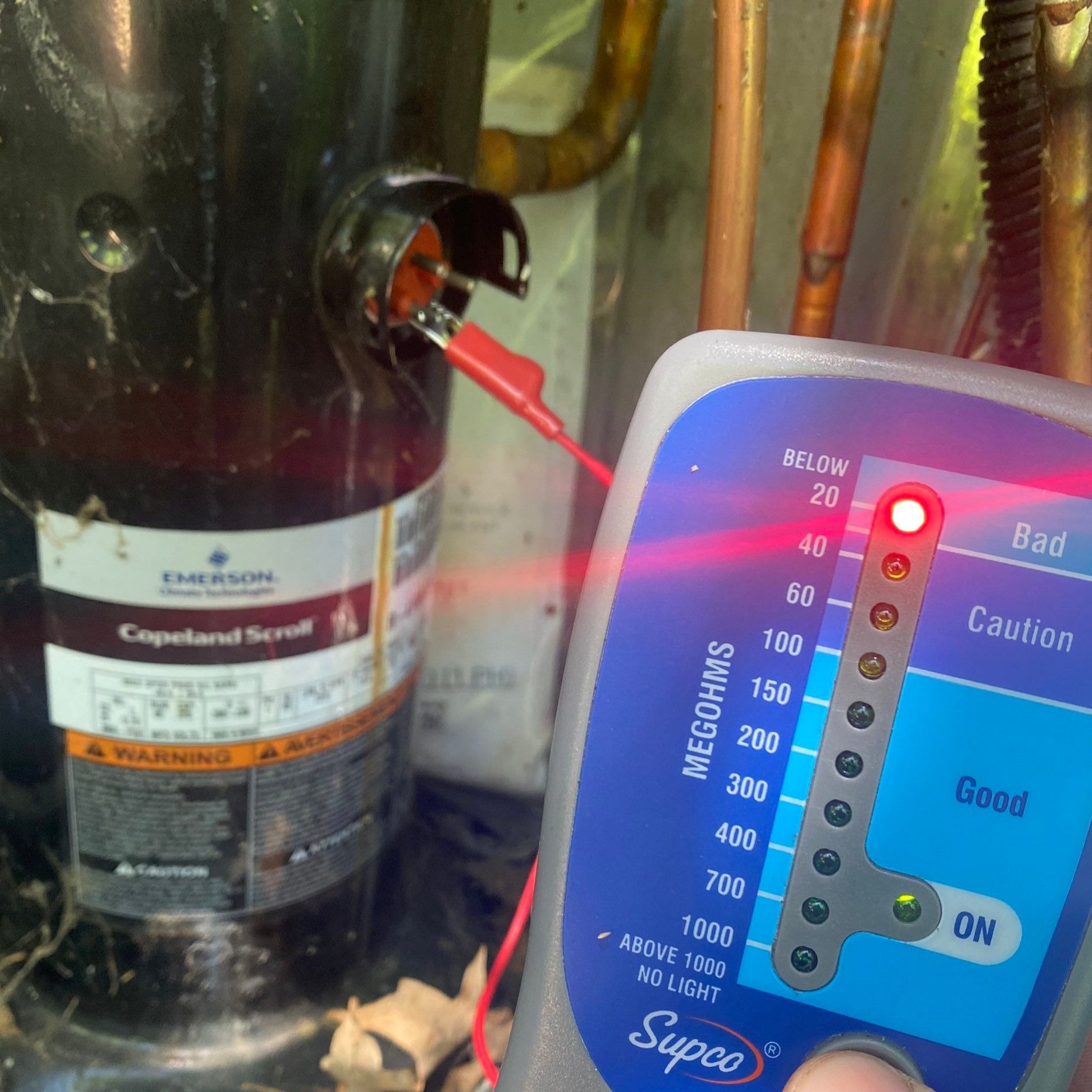
Identifying Refrigerant Leaks
Identifying refrigerant leaks early is essential for maintaining an efficient air conditioning system. Signs of potential refrigerant leaks include weak airflow from vents or ice buildup on the AC unit. These issues often indicate problems with the air handler or other components.
Early recognition of these signs can prevent further damage and ensure timely maintenance. Addressing refrigerant leaks promptly helps maintain the system’s efficiency and prolongs its lifespan.
Cleaning and Replacing Air Filters
Air filters are crucial for preventing dust and other contaminants from accumulating in an air conditioning system. Regular cleaning and replacement of air filters are necessary to ensure optimal airflow and system efficiency. Neglecting maintenance can result in decreased airflow, increased energy usage, and higher energy bills.
Regularly maintained air filters contribute to better indoor air quality and a more efficient HVAC system. Homeowners should check and replace their air filters according to the manufacturer’s recommendations to keep their systems running smoothly.
Professional HVAC Service Recommendations
Hiring a professional HVAC technician is essential when the system fails to maintain a comfortable indoor temperature. Technicians should check refrigerant levels, test for leaks, and ensure all major components function correctly during service visits. They also perform necessary maintenance tasks to preserve the longevity and efficiency of the system.
It is essential to regularly service the compressor and condenser coils. This practice helps reduce the likelihood of needing an early air conditioning replacement. Professional tune-ups keep all parts of the air conditioning system in optimal condition, ensuring your home remains cool and comfortable year-round.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Investing in energy-efficient HVAC systems and components can lead to significant cost savings and reduced environmental impact. Upgrading to a high-efficiency AC unit or installing a smart thermostat optimizes energy usage and lowers energy bills.
Proactive upgrades help maintain consistent performance and save money over time.
High-Efficiency AC Units
High-efficiency AC units offer better indoor comfort while consuming less energy. Investing in these units can lead to substantial savings on energy bills over time. The minimum SEER rating required for AC units sold in southern states is 15, ensuring they meet efficiency standards.
These units not only offer long-term savings but also contribute to a more sustainable environment. By choosing a high-efficiency AC unit, homeowners can enjoy a comfortable indoor climate while reducing their carbon footprint.
Smart Thermostats
Smart thermostats enhance efficiency and comfort by communicating with AC equipment to maintain desired temperatures. These devices allow homeowners to program temperature settings based on daily schedules, optimizing energy use and reducing energy bills.
Installing a smart thermostat can significantly improve the efficiency of an air conditioning system. By adjusting temperatures based on occupancy patterns, smart thermostats ensure that the system operates only when needed, leading to enhanced comfort and energy savings.
Summary
Understanding the essential parts of a home AC system is crucial for maintaining efficiency, comfort, and longevity. From key components like evaporator coils, compressors, and condenser coils to supporting parts such as blower fans, thermostats, and air filters, each plays a vital role in the overall function of the system. Regular maintenance and timely servicing can prevent common issues and ensure optimal performance.
Investing in high-efficiency units and smart thermostats can lead to significant cost savings and improved energy efficiency. By taking proactive steps to understand and maintain your air conditioning system, you can ensure a comfortable and energy-efficient home environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main components of an air conditioning system?
The primary components of an air conditioning system are the evaporator coils, compressor, condenser coils, and expansion valve. Each of these elements plays a crucial role in cooling and circulating air efficiently throughout your space.
How often should I replace my air filter?
Air filters should be replaced every 1-3 months, depending on usage and manufacturer guidelines, to maintain optimal airflow and system efficiency. Regular maintenance is key to ensuring your HVAC system operates effectively.
What are the signs of a refrigerant leak in my AC system?
Signs of a refrigerant leak in your AC system include weak airflow from the vents, ice buildup on the unit, and persistent cooling issues. It is crucial to address these symptoms promptly to ensure optimal system performance.
Why is regular HVAC maintenance important?
Regular HVAC maintenance is essential as it ensures efficient operation, reduces energy consumption, and prevents common issues like dirty coils and malfunctioning fans. This proactive approach ultimately extends the lifespan of your system and enhances indoor comfort.
How can I improve the energy efficiency of my AC system?
To enhance the energy efficiency of your AC system, consider upgrading to a high-efficiency unit, installing a smart thermostat, and ensuring regular maintenance. These steps will lead to cost savings and a smaller environmental footprint.