Troubleshooting Electric Heat
Electric furnace troubleshooting
Today's modern heating system doesn't typically use electric heat as a sole source of warm air. It is typically used to supplement or back up a heat pump.
Electric Furnaces have 3 Functional Components
Heating Element:
The heating element is the core component responsible for generating heat in an electric furnace. When electrical current flows through the heating element, it produces heat that warms the air circulating through the furnace, providing the necessary warmth for the indoor space.
Blower Motor and Fan:
The blower motor and fan work in tandem to circulate the heated air throughout the ductwork and into the living spaces. The motor powers the fan, which draws air over the heating element and then distributes the warm air through the ducts, ensuring even heating throughout the building.
Thermostat:
The thermostat serves as the control center, allowing users to set and regulate the desired temperature. When the temperature falls below the set point, the thermostat signals the furnace to activate, initiating the heating process. Once the desired temperature is reached, the thermostat signals the furnace to shut off, maintaining a comfortable indoor climate.
If your electric furnace is blowing cold air, here is a general guide for electric furnace troubleshooting.
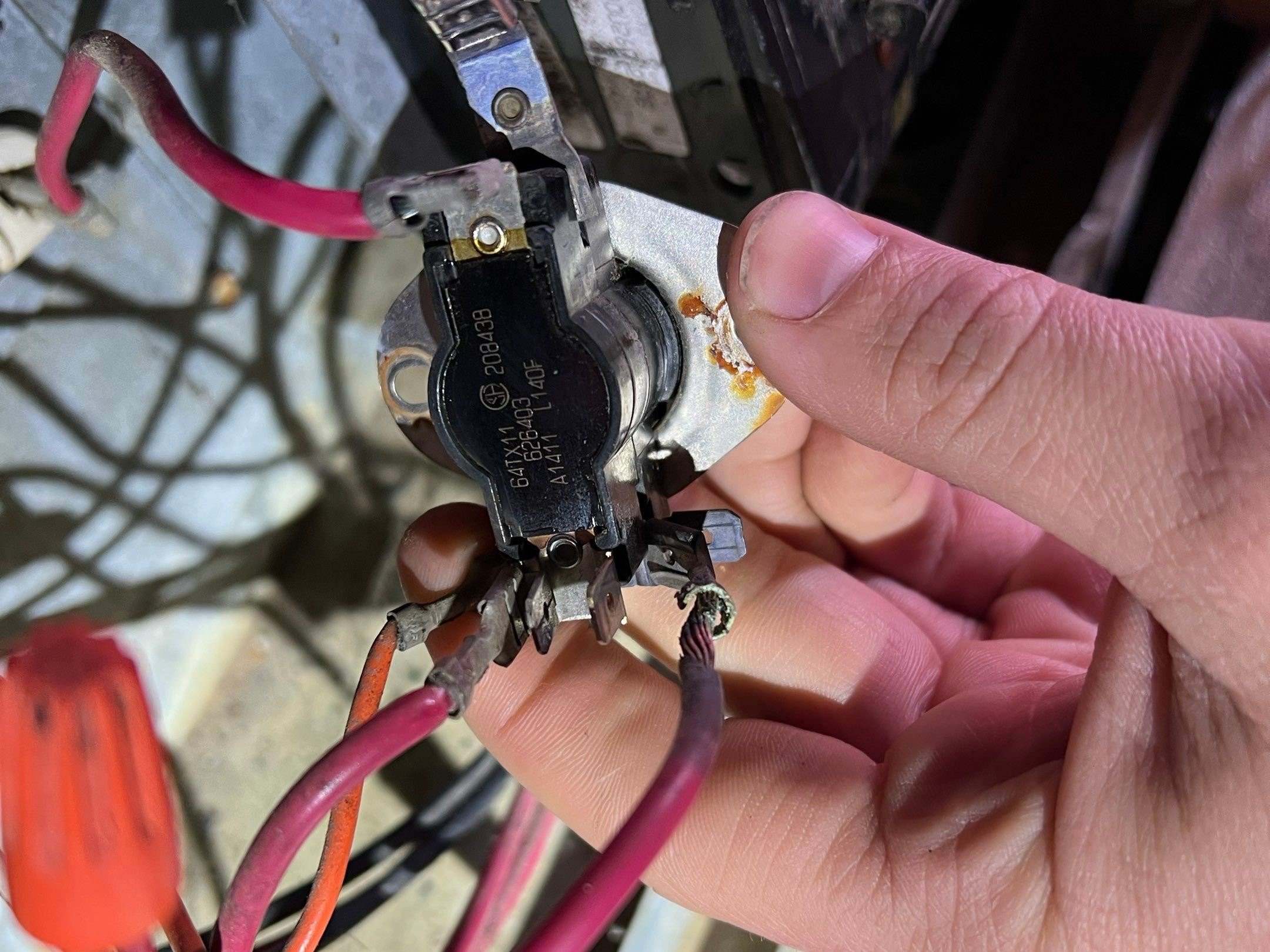
Heating Element Service
Damaged heating sequencer
When performing electrical checks on the heating element in an electric furnace, follow these steps for a concise summary:
Turn Off Power:
Begin by turning off the power to the electric furnace to ensure safety during the inspection.
Access the Heating Element:
Open the access panel to reach the heating element. Refer to the furnace manual for guidance on its location.
Visual Inspection:
Check for visible damage such as cracks, breaks, or discoloration.
Ensure secure connections and inspect for loose wires.
Remove any debris or dust around the heating element.
Use a Multimeter:
Set the multimeter to the resistance or continuity setting.
Test for continuity across the heating element terminals. A reading of continuity indicates a functioning element.
Voltage Check:
With power restored, use the multimeter to check for voltage at the heating element. Ensure the voltage matches the specified rating.
Document Findings:
Note any issues or abnormalities found during the inspection and testing.
Address Issues:
Based on the findings, replace or repair the heating element if necessary.
Consult with a qualified HVAC professional for complex issues or if you're unsure about the repairs.
Secure Access Panel:
Once the checks and any necessary repairs are complete, securely close the access panel.
Always prioritize safety, follow manufacturer guidelines, and exercise caution when working with electrical components. If you encounter difficulties or uncertainties during the electrical checks, seek assistance from a qualified HVAC professional.
Blower Motor and Fan on an Electric Furnace
Dirty blower wheel
Checking the blower motor and fan in an electric furnace involves a series of inspections to ensure proper operation and identify potential issues. Here's a summary of the key checks:
Turn Off Power:
Prioritize safety by turning off the power to the electric furnace. Locate the circuit breaker or switch supplying power and switch it off to prevent electrical accidents.
Inspect for Physical Damage:
Visually examine the blower motor and fan for any signs of physical damage, such as bent blades, cracks, or loose components. Damaged parts may affect performance and create a noisy electric furnace.
Lubricate Moving Parts:
Check the manufacturer's recommendations for lubrication. If required, apply the recommended lubricant to the blower motor bearings and fan shaft according to the guidelines in the furnace's manual.
Check for Obstructions:
Ensure there are no obstructions around the blower fan or inside the ductwork. Debris or foreign objects can impede airflow and cause the motor to work harder, potentially leading to overheating.
Test the Capacitor:
Using a multimeter, check the capacitor connected to the blower motor. A malfunctioning capacitor can result in poor motor performance. Follow safety precautions and discharge the capacitor before testing.
Inspect Wiring and Connections:
Examine the wiring and electrical connections to the blower motor. Look for loose or damaged wires. Tighten any loose connections and replace any damaged wires to ensure proper electrical flow.
Check Motor Amperage:
Use a clamp meter to measure the amperage of the blower motor. Compare the reading to the manufacturer's specifications. If the amperage is significantly higher, it may indicate an issue with the motor.
Test Motor Start and Run Capacitors:
Verify the functionality of the start and run capacitors associated with the blower motor. Replace any faulty capacitors as needed.
Inspect the Fan Blades:
Ensure that the fan blades are clean and free from dirt or debris. Balanced and clean blades contribute to smooth and efficient operation.
Turn the Power On and Observe:
After completing the checks, turn the power back on and observe the blower motor and fan in operation. Listen for any unusual noises and check for proper airflow.
If any issues are identified during these checks, it's recommended to address them promptly. For complex problems or if you're unsure about any aspect of the inspection, seek assistance from a qualified heating and air conditioning professional.
Thermostat on Electric Furnace
Thermostat reading 63 degrees
Checking the thermostat on an electric furnace involves a few key steps to ensure proper functionality and temperature control. Here's a summary of the checks:
Verify Power and Settings:
Ensure that the thermostat has power and is set to the desired temperature. Check the display for any error messages or unusual readings.
Test Temperature Control:
Adjust the thermostat to a temperature higher than the current room temperature. Listen for a click, indicating that the thermostat is signaling the furnace to turn on. Likewise, lowering the temperature should trigger a click, signaling the furnace to turn off.
Inspect Wiring and Connections:
Turn off power to the furnace and thermostat. Open the thermostat cover and inspect the wiring and connections. Look for loose or damaged wires. If any issues are found, consider tightening connections or replacing damaged wires.
Replace Batteries (if applicable):
If the thermostat uses batteries, check and replace them if needed. Low or dead batteries can lead to erratic thermostat behavior.
Check and Calibrate Thermostat:
Use a separate thermometer to verify the accuracy of the thermostat's temperature readings. If there is a significant discrepancy, consider recalibrating the thermostat following the manufacturer's instructions.
Ensure Proper Placement:
Confirm that the thermostat is installed in an optimal location. Avoid placing it near drafty areas, heat sources, or in direct sunlight, as this can affect temperature readings and the furnace's operation.
Review Program Settings (if programmable):
If the thermostat is programmable, review and adjust the programmed settings as needed. Ensure that the programmed schedule aligns with your heating preferences.
Test Fan Operation:
Set the thermostat to the "Fan" mode and check if the blower fan operates properly. This helps ensure that the fan can distribute warm air effectively when the furnace is running.
Consider Thermostat Upgrades:
If the thermostat is outdated or exhibiting persistent issues, consider upgrading to a newer model with advanced features, such as programmability and smart home integration.
Regular checks of the thermostat are crucial for maintaining a comfortable and efficient heating system. If problems persist or if you're unsure about any aspect of the thermostat's operation, consult the thermostat's manual or seek professional assistance.
Don't forget the basics
Before you call an HVAC professional, check some of the basics:
Thermostat setting
Make sure your thermostat is set properly and "ON".
Air filter cleanliness
Your furnace filter should be changed or cleaned at least quarterly.
Circuit breakers or fuses
Check your circuit breaker or fuse panel for a tripped breaker or blown fuse possibly caused by a power surge. The furnace should be on a separate fuse or circuit breaker.
Call if you need help
If checking the basics doesn't get your system back on track, call an expert. Working on your electric furnace is never recommended. Electrical shock is a definite danger.